Definition
Ansible uses different inventory plugins to manage data transferred from files or scripts and convert it to JSON format
In general there are 3 types of inventory:
Static— plain fileDirectory— directory with filesDynamic— executable file
At the same time if you can use second (Directory) type with first (Static) type and third (Dynamic) type simultaneously, and the resulting inventory will be a collection of all inventories from this directory.
Supported formats for Static inventory are limited by inventory plugins, which you could write by yourself, however in ansible.builtin (Ansible core) you can only use:
yaml-ansible.builtin.yamljson-ansible.builtin.yaml(let me remind you that correctly written JSON is also YAML)ini-ansible.builtin.initoml-ansible.builtin.toml
Most often used are yaml and ini, but according to ansible best-practice you shoud use yaml format
All types of plugins for inventory can be found here (https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/index_inventory.html)
Practice
As an example, I will demonstrate the same static inventory in different formats:
inventory.ini:
[awx_root]
awx ansible_user=admin ansible_host=192.0.2.10
inventory.toml:
[all.vars]
ansible_user = "admin"
[awx_root.hosts]
awx = { ansible_host = "192.0.2.10" }
inventory.yml:
---
all:
vars:
ansible_user: admin
hosts:
awx:
ansible_host: 192.0.2.10
children:
awx_root:
hosts:
awx:
inventory.json:
{
"all": {
"vars": {
"ansible_user": "admin"
},
"hosts": {
"awx": {
"ansible_host": "192.0.2.10"
}
},
"children": {
"awx_root": {
"hosts": {
"awx": null
}
}
}
}
}
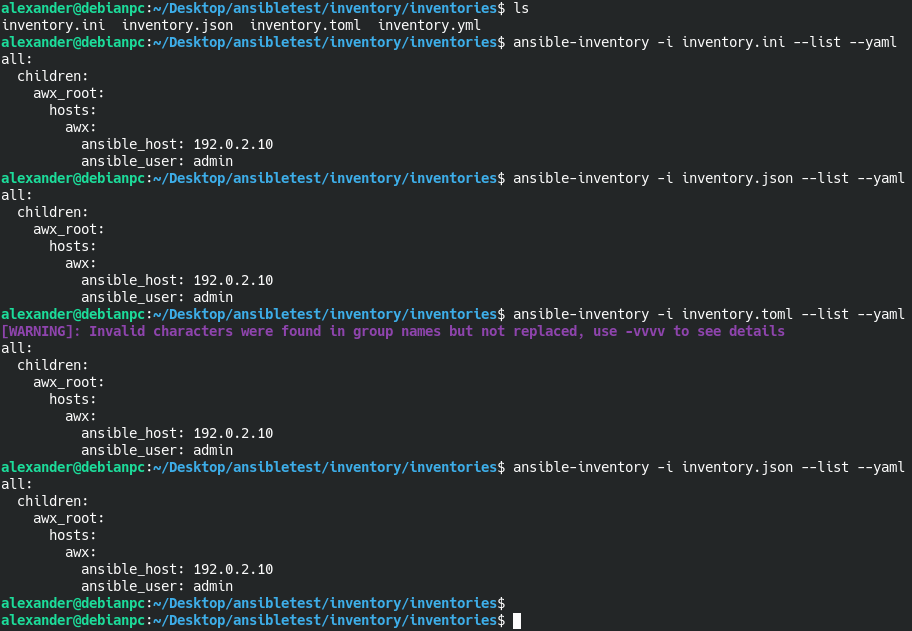
Using the command ansible-inventory -i <имя_файла> --list you can check all 4 files and see that the resulting JSON response will be the same (you can add the --yaml flag for convenient output in yaml format)
A more detailed description with examples for dynamic inventories will be in a separate article.